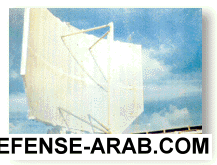
رد: الرادارات العاملة بالقوات المسلحة المصرية
هناك شق تقني سأتحدث به
رابط
هناك صفر زائد فارتفاع كشفه 100.000 قدم فقط
هناك شق تقني سأتحدث به
tps-59; (v)3 - 3d tactical missile defense
description: A land-based/long-range, 3d phased-array radar for the us marine landing force in an amphibious environment, and support of taoc-85 operations.
Frequency: 1.215 - 1.4 ghz, l-band, 14% agile bandwidth
power: 46 kw, 54 kw (with upgraded 100 watt peak power modules), average 8.3 kw , effective radiated power 270 mw
range: 4 to 300 nautical miles. Tactical ballistic missiles, 400 nautical miles; cruise missiles and aircraft, 300 nautical miles
accuracy (100 nm): 100 feet
resolution (100 nm): 140 feet
vertical coverage: 1,000,000 feet
horizontal coverage: 360 degrees
probability of detection: 90% 1m2 target within 200 nm.
Antenna: 360 degree azimuth coverage,
speed: 6 rpm or 12 rpm
height: 30 ft
width:15 ft
beamwidth: 1.7° (monopulse), 1.4° (low angle)
sidelobe reduction: 55 db
weight:
System: 28,000 lb
shelter dimensions:
Radar control group: 87 x 147 x 85 in
signal processor group: 87 x 147 x 85 in
manufacturer: General electric; lockheed martin
notes: Marine corps radar; early warning; situational awareness radar; an estimated 21 tps-59(v) radars were produced, nine fms orders, and nine tps-59m/34 radars have been produced. Cost: $12.6 million.
Notes: The tps-59(v) system is a phased-array tactical radar designed to provide long-range surveillance for the tactical air operations center (taoc-85 or tyq-23(v)). The radar has a solid-state transmitter and a rotating planar array antenna. The displays and processors are housed in two standard s-280 military shelters that include a uyk-7(v) general-purpose digital computer and three 45 kw diesel generators.
The antenna uses 54 identical row/feed networks, 27 power supplies, and a digital signal processor to control the beam pattern and process the returned signals. The smaller tps-59m/34 uses 34 identical row/feed networks and 17 power supplies. The low-level transceivers include power supplies, transmitters, preamplifiers, phase shifters, duplex ers, and logic control circuitry. There is one column feed assembly and one monitor feed assembly in the tps-59(v). There are three and one, respectively, in the tps-59m/34. The feeds distribute power vertically on the antenna scanning the elevation plane.
During operation, the self-erecting array antenna rotates mechanically in azimuth while a pencil beam electronically scans in elevation from 0° to 19°. This is the key to the radar’s 3d capability. The scanning covers the specified surveillance volume in a raster-scan pattern.
Two basic surveillance waveforms are used: One for the short-range interval (5.5 to 185 km) which requires 11 pencil beams, and another for the long-range interval (from 185 km to the limits of coverage) which requires eight pencil beams.
The system was designed to counter the effects of multi-path propagation. For optimal system performance, a special weather mode adjusts energy management and processing every five minutes according to weather conditions.
Three trailer assemblies carry the system. The radar can be transported by helicopter, 2.5 ton truck, c-130 aircraft, rail, or seagoing vessel.
History:
Month year major development
1972 first development contract awarded
1976/77 usmc acceptance testing begins
1980 production contract
1985 delivery of 10 tps-59 radars to navelex
1985/86 usmc/usaf complete operational testing
1989 initial operational capability of taoc-85
3q fy94 adcp requirements document due
fy95/1996 r&d into missile defense upgrades
fy96/1997 missile defense upgrade procurement
dec 1999 modification studies completed; contract awarded to upgrade five egyptian tps‑59(v)2s
2001 egyptian tps-59m/34 upgrades contracted
feb 2003 egyptian upgrades to be completed
brochure 1; photostps-59; (v)3 - 3d tactical missile defense
description: A land-based/long-range, 3d phased-array radar for the us marine landing force in an amphibious environment, and support of taoc-85 operations.
Frequency: 1.215 - 1.4 ghz, l-band, 14% agile bandwidth
power: 46 kw, 54 kw (with upgraded 100 watt peak power modules), average 8.3 kw , effective radiated power 270 mw
range: 4 to 300 nautical miles. Tactical ballistic missiles, 400 nautical miles; cruise missiles and aircraft, 300 nautical miles
accuracy (100 nm): 100 feet
resolution (100 nm): 140 feet
vertical coverage: 1,000,000 feet
horizontal coverage: 360 degrees
probability of detection: 90% 1m2 target within 200 nm.
Antenna: 360 degree azimuth coverage,
speed: 6 rpm or 12 rpm
height: 30 ft
width:15 ft
beamwidth: 1.7° (monopulse), 1.4° (low angle)
sidelobe reduction: 55 db
weight:
System: 28,000 lb
shelter dimensions:
Radar control group: 87 x 147 x 85 in
signal processor group: 87 x 147 x 85 in
manufacturer: General electric; lockheed martin
notes: Marine corps radar; early warning; situational awareness radar; an estimated 21 tps-59(v) radars were produced, nine fms orders, and nine tps-59m/34 radars have been produced. Cost: $12.6 million.
Notes: The tps-59(v) system is a phased-array tactical radar designed to provide long-range surveillance for the tactical air operations center (taoc-85 or tyq-23(v)). The radar has a solid-state transmitter and a rotating planar array antenna. The displays and processors are housed in two standard s-280 military shelters that include a uyk-7(v) general-purpose digital computer and three 45 kw diesel generators.
The antenna uses 54 identical row/feed networks, 27 power supplies, and a digital signal processor to control the beam pattern and process the returned signals. The smaller tps-59m/34 uses 34 identical row/feed networks and 17 power supplies. The low-level transceivers include power supplies, transmitters, preamplifiers, phase shifters, duplex ers, and logic control circuitry. There is one column feed assembly and one monitor feed assembly in the tps-59(v). There are three and one, respectively, in the tps-59m/34. The feeds distribute power vertically on the antenna scanning the elevation plane.
During operation, the self-erecting array antenna rotates mechanically in azimuth while a pencil beam electronically scans in elevation from 0° to 19°. This is the key to the radar’s 3d capability. The scanning covers the specified surveillance volume in a raster-scan pattern.
Two basic surveillance waveforms are used: One for the short-range interval (5.5 to 185 km) which requires 11 pencil beams, and another for the long-range interval (from 185 km to the limits of coverage) which requires eight pencil beams.
The system was designed to counter the effects of multi-path propagation. For optimal system performance, a special weather mode adjusts energy management and processing every five minutes according to weather conditions.
Three trailer assemblies carry the system. The radar can be transported by helicopter, 2.5 ton truck, c-130 aircraft, rail, or seagoing vessel.
History:
Month year major development
1972 first development contract awarded
1976/77 usmc acceptance testing begins
1980 production contract
1985 delivery of 10 tps-59 radars to navelex
1985/86 usmc/usaf complete operational testing
1989 initial operational capability of taoc-85
3q fy94 adcp requirements document due
fy95/1996 r&d into missile defense upgrades
fy96/1997 missile defense upgrade procurement
dec 1999 modification studies completed; contract awarded to upgrade five egyptian tps‑59(v)2s
2001 egyptian tps-59m/34 upgrades contracted
feb 2003 egyptian upgrades to be completed
brochure 1; photos
رابط
هناك صفر زائد فارتفاع كشفه 100.000 قدم فقط
التعديل الأخير: