انت الان تضع السو 35 فوق الاف 15 مع العلم ان العكس هو الصحيح اذا خسرت الاف 15 ب 8-0 فاعلم ان السو 35 سوف تخسر ب 16-0او سوخوي 35 فهي الاقرب لها في القوه والعظمه والهيبه
تثبيت التطبيق
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
ملاحظة: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
أنت تستخدم أحد المتصفحات القديمة. قد لا يتم عرض هذا الموقع أو المواقع الأخرى بشكل صحيح.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
الاف 35 A تهزم الاف 15 E بنسبة 8:0 في مناورات قتال جوية ..
- بادئ الموضوع صقر الامارات
- تاريخ البدء
ليس سناك ... تميزها في بصماتها المنخفضة يرقيها لمرتبة Main Course + تحلية .
هكذا هي بين مقاتلات الجيل الرابع+ والذي لايبدو انه مؤهل للتغلب على الجيل الخامس .
انت متناقض في مشاركة لك انكرت شبحية الرافال والان تقول منخفضة البصمة طبعاً استناد على نظرية الحجم الصغير الباطلة
طبعاً من أهم مزايا الجيل الخامس البصمة المنخفضة
طبعاً من أهم مزايا الجيل الخامس البصمة المنخفضة
انت متناقض في مشاركة لك انكرت شبحية الرافال والان تقول منخفضة البصمة طبعاً استناد على نظرية الحجم الصغير الباطلة
طبعاً من أهم مزايا الجيل الخامس البصمة المنخفضة
صديقي لاتهاجمني فهذا من مدمرات الصداقة والاخوة الرائعة التي نحظى بها هنا
اولا تعال اقبل رأسك واعطيك وردة ,,, ومن ثم اسمح لي بالتوضيح :
1- كاميكازي لم يقل في يوم ان الرافال شبحية بل منخفضة البصمات ( قياسا على ما اعتقده وبعض مما قرأت بالمصادر ,, وليس جزما بشيء مؤكد كونه لاتوجد معلومات رسمية بهذا الخصوص , والامر مماثل للجميع شرقا وغربا شمالا وجنوبا )
2- كاميكازي يحبك في الله ,,, فهل تحبه انت ايضا !!
في احد الاختبارات داخل امريكا
لم تكتشفها الرادارات الامريكيه الا بعد ان كشفت الطائرة عن نفسها متعمدة
عندما طارت ... اختفت
شبحيتها الزائدة شكلت تحديا كبيرا في التدريب معها
The F-35 is so stealthy, it produced training challenges, pilot says
 Phillip Swarts, Air Force Times5:04 a.m. EDT July 31, 2016
Phillip Swarts, Air Force Times5:04 a.m. EDT July 31, 2016
AIR FORCE TIMES
Air Force Pilots, Maintainers on F-35 Pros and Cons
“When we go to train, it’s really an unfair fight for the guys who are simulating the adversaries,” Watkins continued. “We’ve been amazed by what we can do when we go up against fourth-gen adversaries in our training environment, in the air and on the ground.”
Watkins said he can take four F-35s and “be everywhere and nowhere at the same time because we can cover so much ground with our sensors, so much ground and so much airspace. And the F-15s or F-16s, or whoever is simulating an adversary or red air threat, they have no idea where we’re at and they can’t see us and they can’t target us.”
“That’s a pretty awesome feeling when you’re going out to train for combat,” Watkins concluded, "to know that your pilots are in an unfair fight.”
The pilots and crews at Hill have been putting the new fifth-generation fighter through its paces, in preparation for top Air Force brass declaring the plane operationally ready — a move expected within days.
The Air Force’s variant of the F-35 will make its first appearance at the famous Red Flag training exercise at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada, in January 2017, Watkins told Air Force Times. Marine Corps F-35Bs have already reached initial operating capability and participated in the exercise this year.
AIR FORCE TIMES
Top Marine aviator: F-35B is ready for war
Lt. Col. Steven Anderson, the 388th Maintenance Group deputy commander, said all the boxes have been checked for Hill F-35s to reach IOC, and that the base will be ready to send six-ship packages of the aircraft wherever they’re needed in the world.
“For most of us, this is a once in a lifetime opportunity to bed down a new weapon set and make it employable and bring this capability for the defense of our nation,” Anderson said. “Everyone from the youngest airmen on up through our wing commanders is totally invested in this program. We are all excited and very motivated for what we’ve accomplished over the last year and what we’re going to accomplish in the future.”
Hill now has 21 pilots ready to fly, with another three going through final certification training, Anderson said. Some 222 maintainers are also ready, with another 150 in training. The base has 15 F-35s now, with a 16th scheduled to be delivered in late August. Eventually, the base is looking to set up three full squadrons with a total of 72 aircraft by 2019.
Anderson said the base isn’t expecting any problems with getting enough maintainers or pilots to operate the planes.
“We don’t see any shortfalls in our maintenance and pilots right now,” he said. “We can project up to 18 months out to see where our pilots and maintainers are coming from, and we will have enough to stand up this unit. IOC, for us, it’s just getting us out of the starting gate.”
http://www.airforcetimes.com/story/...uced-training-challenges-pilot-says/87760454/
لكن الشبحية الرادارية هي جزء من المستويات المتعددة للشبحية ومنها الشبحية على مستوى الابنعاثات الكهرومغناطيسية وكذلك الشبحية على مستوى الحرارة
موقع Defense Aerospace نشر تقريرا عن حدود لشبحية الاف 35 من ناحية البصمة الحرارية ,,, راجع الفيديو ادناه ,, يبين مشكلة الاف 35 من هذه الناحية
F-35 in FLIR Thermal!
(Source: FLIR Systems; issued August 11, 2016)
It’s always amazing to see complex machinery and the heat they generate through the lens of a thermal camera, the Lockheed Martin F-35 is no exception! The F-35 is a state-of-the-art stealth multirole fighter, and this particular model allows for vertical landing (as you’ll see in the “hottest” part of the video!)
This footage was captured using the FLIR Star SAFIRE 380-HDc during a flight demonstration at last month’s Farnborough International Air Show.
(EDITOR’S NOTE: The footage above illustrates why the F-35 is easily detectable despite its much-hyped radar “stealth:” it generates so much heat that it is visible at long ranges by thermal imaging sensors, such as the infra-red scan and track (IRST) sensors fitted to most combat aircraft made outside the US.
It also begs the question of how Lockheed designers – and the Pentagon -- can have believed their own “stealth” claims to the point of ignoring the F-35’s infra-red signature, which negates all gains made in the radar spectrum.
Incidentally, it also makes one wonder how US military aviation chiefs could have accepted an entire generation of combat aircraft without IRST sensors they are now belatedly trying to retrofit.
In the video, the switch from visible to thermal imaging, at the 10 second mark, is especially telling (hotter is whitest).
To coin a phrase, it stands out like a blowtorch in a dark room.
Throughout its modest flight display, the aircraft – an F-35B STOVL variant -- generated an incredible amount of heat, which makes it easily detectable from any angle by any thermal imaging sensor, including IR binoculars and sights that are widely distributed on the modern battlefield.)
-ends-
http://www.defense-aerospace.com/ar...footage-shows-f_35’s-stealth-limitations.html
الطائرات من الجيل الرابع ++ المزودة بانظمة رصد كهروبصري ستراها من خلال البصمه الحرارية الضخمه و يمكن نشر انظمة رصد كهروبصري فعالة على السفن الحربية و على الحدود لتحقيق الانذار المبكر للقواعد الجوية و الدفاع الجوى و تزويد انظمة الدفاع الجوى بانظمة كهروبصرية


الطائرات من الجيل الرابع ++ المزودة بانظمة رصد كهروبصري ستراها من خلال البصمه الحرارية الضخمه و يمكن نشر انظمة رصد كهروبصري فعالة على السفن الحربية و على الحدود لتحقيق الانذار المبكر للقواعد الجوية و الدفاع الجوى و تزويد انظمة الدفاع الجوى بانظمة كهروبصرية

هناك ما هو واعد اكثر فيما يخص انظمة الرؤية الكهروبصرية الامامية ( FSO على سبيل المثال )
اقرأ الفقرة 6:41 من كتاب Indian Defense Review المجلد 23
ستجد ان FSO الرافال استطاع الاطباق على هدف ومباغتته بالميكا الحراري ( بدون تشغيل الرادار )
https://books.google.ae/books?id=Cj...EINDAD#v=onepage&q=rafale fso mica ir&f=false
هذه اشارة مهمة جدا - لكون ان الرادار لم يتم تشغيله - ومع ذلك تم تدمير الهدف بنجاح بوسطة توليفة منظومة الرصد الكهروبصرية والميكا الحراري
ميزة IRST او Infra Red Search & Track وقيام ثاليس بذكر ان لها ( قدرات ) جو-جو و جو-ارض ,, له معاني كبيرة

توليفة قاتلة
+
=
القتل الصامت
الكاتب الفرنسي يتعجب من تجاهل و اهمال الامريكان انظمة الرصد الكهروبصري على جيل كامل من الطائرات و الامريكان بدئوا مؤخرا بتركيب بود كهروبصري خارجي على مقاتلات اف 16 و اف 15 و ارى ان الامارات حسنا فعلا اذ اضافت منظومة رصد كهروبصرية على الفالكون الاماراتية حصريا و هو ما يؤهلها لمجابهة مخاطر الجيل الخامس ايضا بقدر مميز خصوصا فى ظل منظومة حماية تؤهلها للتخلص من الصواريخ جو جو بالتشويش على باحثه لتحقيق الاقتراب المناسب للاغلاق كهروبصريا و اتمنى ان تزود الامارات الديزرت فالكون لديها بالميكا الحراري او نظير روسي اخر و هو R-27 ابعد فى المدي .هناك ما هو واعد اكثر فيما يخص انظمة الرؤية الكهروبصرية الامامية ( FSO على سبيل المثال )
اقرأ الفقرة 6:41 من كتاب Indian Defense Review المجلد 23
ستجد ان FSO الرافال استطاع الاطباق على هدف ومباغتته بالميكا الحراري ( بدون تشغيل الرادار )
https://books.google.ae/books?id=CjIYCRvbaKoC&pg=PA73&lpg=PA73&dq=rafale+fso+mica+ir&source=bl&ots=wgrLuyobZH&sig=R5J20SjENnZwc6aCw4AN_f_jL8k&hl=ar&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwitz6ruyMLOAhXIK8AKHUYuBCcQ6AEINDAD#v=onepage&q=rafale fso mica ir&f=false
هذه اشارة مهمة جدا - لكون ان الرادار لم يتم تشغيله - ومع ذلك تم تدمير الهدف بنجاح بوسطة توليفة منظومة الرصد الكهروبصرية والميكا الحراري
ميزة IRST او Infra Red Search & Track وقيام ثاليس بذكر ان لها ( قدرات ) جو-جو و جو-ارض ,, له معاني كبيرة

توليفة قاتلة

+

=
القتل الصامت
الفرنسيين يعرضون ميزة اضافية في بود التاليوس و هى قدرة الرصد و الاقفال جو جو لتجهيز الميراج و غيرها بهذا البود بخلاف طبعا لدورة العظيم في الرصد جو ارض و التوجيه الدقيق ايضا بالاضافة لكونه ايضا مركز اتصالات و دعم لجعل القوات او المقاتلات الصديقة تري ما يرصده هذا البود

تاليوس في مهام جو جو


الكاتب الفرنسي يتعجب من تجاهل و اهمال الامريكان انظمة الرصد الكهروبصري على جيل كامل من الطائرات و الامريكان بدئوا مؤخرا بتركيب بود كهروبصري خارجي على مقاتلات اف 16 و اف 15 و ارى ان الامارات حسنا فعلا اذ اضافت منظومة رصد كهروبصرية على الفالكون الاماراتية حصريا و هو ما يؤهلها لمجابهة مخاطر الجيل الخامس ايضا بقدر مميز خصوصا فى ظل منظومة حماية تؤهلها للتخلص من الصواريخ جو جو بالتشويش على باحثه لتحقيق الاقتراب المناسب للاغلاق كهروبصريا و اتمنى ان تزود الامارات الديزرت فالكون لديها بالميكا الحراري او نظير روسي اخر و هو R-27 ابعد فى المدي .
الفرنسيين يعرضون ميزة اضافية في بود التاليوس و هى قدرة الرصد و الاقفال جو جو لتجهيز الميراج و غيرها بهذا البود بخلاف طبعا لدورة العظيم في الرصد جو ارض و التوجيه الدقيق ايضا بالاضافة لكونه ايضا مركز اتصالات و دعم لجعل القوات او المقاتلات الصديقة تري ما يرصده هذا البود

توليفة السايد وايندر والـOSF على الاف 16 بلوك 60 يمكن ان تلعب دورا في السدّ الجزئي لهذا الاحتياج لحين تطوير مدى السايد وايندر ليصبح قريب/بعيد المدى
او كما تفضلت استاذي ,, دمج الميكا IR او البدائل الاخرى المتوفرة من نفس الرؤوس الباحثة ..
فيما يخص الميراج ,, لا اعرف ان كانت حاوية نهار ( NAHAR ) و شهاب ( Shehab ) وهي اشتقاق من الداموكليس ,, يمكنها ان تلعب دورا شبيها ..
NAHAR تخصصها Forward Looking Infra-Red system
http://www.dassault-aviation.com/en/defense/customer-support/mirage-2000/mirage-2000-9/
http://defense-arab.com/vb/threads/39475/
لو كان بمقدورها لعب نفس دور حزمة الرافال - وهناك اشارة في رابط داسو ان الميراج-9 تم تطويرها باستلهام تطويرات برنامج الرافال وتكنولوجياتها - وبالتالي قد تصح النظرية ..
وان صحّت ... لربما تكون الميراج-9 بالفعل قادرة على استخدام نفس توليفة القتل الصامت ...
الحاوية + الميكا الحراري
والله اعلم
يكفي F15 شرفا ان صح خبر هذه المناورات ان الاختيار وقع عليها لمنازلة المقاتلة الشبحية F35
لماذا لم يتم اختيار F16 على سبيل المثال مع ان F16 هي الاقرب لفئة F35 ؟؟
الاف 35 نازلت الاف 16 بالفعل لكن تفوقت الاف 16
F-35 Joint Strike Fighter vs. F-16; The F-16 Wins in a Dogfight, But Does It Matter?
January 19, 2016 Comments Offon F-35 Joint Strike Fighter vs. F-16; The F-16 Wins in a Dogfight, But Does It Matter? 26,693 Views
To Replace Or Not To Replace, That Is the Question
The F-16 has been tried and true for years, but it is to be replaced by the most expensive conventional weapons project for the DOD F-35 project from hell that has cost the United States over $350 Billion. The recent buzz is all about the maneuverable, external weapons loaded F-16 winning over the stealth loaded F-35 in a dog fight, but does that mean the Air Force will put a kibosh on the F-35? Of course not if the opinions of the USAF pilots of the F-35 count. Breaking Defense has a current comparison and arguments for the use of both.
The F-35 is touted to be able to spot and neutralize the enemy before the enemy can spot it. Breaking Defense had a rare interview with the Air Force in 2014 with one discussion leading to what the F-35 can do in the first 10 days of war,
“Gen. Hostage noted during our interview that the F-35 pilot who engages in a dogfight has either made a mistake or been very unlucky. Shooting down other planes using kinetics is only one role of the F-35. Perhaps air forces around the world are going to have to come up with a new honor other than ace to define those who fly the F-35. What should a pilot be awarded for outsmarting the best air defense systems in the world (like the Russian S-300 and S-400) or injecting something like Stuxnet into the enemy’s command and control system? So much of what this aircraft will do has nothing to do with shooting down another pilot that we may need a new term.”
But for hot dog fights, it is the F-16, not the F-35 that is the aircraft of choice.
“The F-35 doesn’t have the altitude, doesn’t have the speed [of the F-22], but it can beat the F-22 in stealth,” Hostage told Breaking Defense, “The F-35 is geared to go out and take down the surface targets.” In fact, it takes eight F-35s to do what two F-22s can accomplish in the early stages of a war.

TYNDALL AIR FORCE BASE, Fla. — Lt. Col. Mike Cosby, 177th Fighter Wing commander, flies an F-16C block 25 aircraft from here to Atlantic City International Airport, N.J. The wing participated in Combat Archer training at Tyndall. (U.S. Air Force photo by Master Sgt. Don Taggart)
Take a look at what the Air Force official information the USAF wants public on both aircraft is below and more from Breaking defense below:
F-16
Mission
The F-16 Fighting Falcon is a compact, multi-role fighter aircraft. It is highly maneuverable and has proven itself in air-to-air combat and air-to-surface attack. It provides a relatively low-cost, high-performance weapon system for the United States and allied nations.
Features
In an air combat role, the F-16’s maneuverability and combat radius (distance it can fly to enter air combat, stay, fight and return) exceed that of all potential threat fighter aircraft. It can locate targets in all weather conditions and detect low flying aircraft in radar ground clutter. In an air-to-surface role, the F-16 can fly more than 500 miles (860 kilometers), deliver its weapons with superior accuracy, defend itself against enemy aircraft, and return to its starting point. An all-weather capability allows it to accurately deliver ordnance during non-visual bombing conditions.
In designing the F-16, advanced aerospace science and proven reliable systems from other aircraft such as the F-15 and F-111 were selected. These were combined to simplify the airplane and reduce its size, purchase price, maintenance costs and weight. The light weight of the fuselage is achieved without reducing its strength. With a full load of internal fuel, the F-16 can withstand up to nine G’s — nine times the force of gravity — which exceeds the capability of other current fighter aircraft.
The cockpit and its bubble canopy give the pilot unobstructed forward and upward vision, and greatly improved vision over the side and to the rear. The seat-back angle was expanded from the usual 13 degrees to 30 degrees, increasing pilot comfort and gravity force tolerance. The pilot has excellent flight control of the F-16 through its “fly-by-wire” system. Electrical wires relay commands, replacing the usual cables and linkage controls. For easy and accurate control of the aircraft during high G-force combat maneuvers, a side stick controller is used instead of the conventional center-mounted stick. Hand pressure on the side stick controller sends electrical signals to actuators of flight control surfaces such as ailerons and rudder.
Avionics systems include a highly accurate enhanced global positioning and inertial navigation systems, or EGI, in which computers provide steering information to the pilot. The plane has UHF and VHF radios plus an instrument landing system. It also has a warning system and modular countermeasure pods to be used against airborne or surface electronic threats. The fuselage has space for additional avionics systems.
Background
The F-16A, a single-seat model, first flew in December 1976. The first operational F-16A was delivered in January 1979 to the 388th Tactical Fighter Wing at Hill Air Force Base, Utah.
The F-16B, a two-seat model, has tandem cockpits that are about the same size as the one in the A model. Its bubble canopy extends to cover the second cockpit. To make room for the second cockpit, the forward fuselage fuel tank and avionics growth space were reduced. During training, the forward cockpit is used by a student pilot with an instructor pilot in the rear cockpit.
All F-16s delivered since November 1981 have built-in structural and wiring provisions and systems architecture that permit expansion of the multirole flexibility to perform precision strike, night attack and beyond-visual-range interception missions. This improvement program led to the F-16C and F-16D aircraft, which are the single- and two-place counterparts to the F-16A/B, and incorporate the latest cockpit control and display technology. All active units and many Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve units have converted to the F-16C/D.
The F-16 was built under an unusual agreement creating a consortium between the United States and four NATO countries: Belgium, Denmark, the Netherlands and Norway. These countries jointly produced with the United States an initial 348 F-16s for their air forces. Final airframe assembly lines were located in Belgium and the Netherlands. The consortium’s F-16s are assembled from components manufactured in all five countries. Belgium also provides final assembly of the F100 engine used in the European F-16s. Recently, Portugal joined the consortium. The long-term benefits of this program will be technology transfer among the nations producing the F-16, and a common-use aircraft for NATO nations. This program increases the supply and availability of repair parts in Europe and improves the F-16’s combat readiness.
USAF F-16 multirole fighters were deployed to the Persian Gulf in 1991 in support of Operation Desert Storm, where more sorties were flown than with any other aircraft. These fighters were used to attack airfields, military production facilities, Scud missiles sites and a variety of other targets.
During Operation Allied Force, USAF F-16 multirole fighters flew a variety of missions to include suppression of enemy air defense, offensive counter air, defensive counter air, close air support and forward air controller missions. Mission results were outstanding as these fighters destroyed radar sites, vehicles, tanks, MiGs and buildings.
Since Sept. 11, 2001, the F-16 has been a major component of the combat forces committed to the Global War on Terrorism flying thousands of sorties in support of operations Noble Eagle (Homeland Defense), Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan and Iraqi Freedom
General Characteristics
Primary Function: Multirole fighter
Contractor: Lockheed Martin Corp.
Power Plant: F-16C/D: one Pratt and Whitney F100-PW-200/220/229 or General Electric F110-GE-100/129
Thrust: F-16C/D, 27,000 pounds
Wingspan: 32 feet, 8 inches (9.8 meters)
Length: 49 feet, 5 inches (14.8 meters)
Height: 16 feet (4.8 meters)
Weight: 19,700 pounds without fuel (8,936 kilograms)
Maximum Takeoff Weight: 37,500 pounds (16,875 kilograms)
Fuel Capacity: 7,000 pounds internal (3,175 kilograms); typical capacity, 12,000 pounds with two external tanks (5443 kilograms)
Payload: Two 2,000-pound bombs, two AIM-9, two AIM-120 and two 2400-pound external fuel tanks
Speed: 1,500 mph (Mach 2 at altitude)
Range: More than 2,002 miles ferry range (1,740 nautical miles)
Ceiling: Above 50,000 feet (15 kilometers)
Armament: One M-61A1 20mm multibarrel cannon with 500 rounds; external stations can carry up to six air-to-air missiles, conventional air-to-air and air-to-surface munitions and electronic countermeasure pods
Crew: F-16C, one; F-16D, one or two
Unit cost: F-16A/B , $14.6 million (fiscal 98 constant dollars); F-16C/D,$18.8 million (fiscal 98 constant dollars)
Initial operating capability: F-16A, January 1979; F-16C/D Block 25-32, 1981;
F-16C/D Block 40-42, 1989; and F-16C/D Block 50-52, 1994
Inventory: Total force, F-16C/D, 1018
F-35

Luke Air Force Base’s first F-35 Lightning II flies overhead March 10, 2014, before it lands on base for the first time. The aircraft is the first of 144 F-35s that will eventually be assigned to the base. (U.S. Air Force photo/Staff Sgt. Darlene Seltmann)
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole fighters undergoing testing and final development by the United States. The fifth generation combat aircraft is designed to perform ground attack, aerial reconnaissance, and air defense missions. The F-35 has three main models: the F-35A conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) variant, the F-35B short take-off and vertical-landing (STOVL) variant, and the F-35C carrier-based Catapult Assisted Take-Off Barrier Arrested Recovery (CATOBAR) variant.
Mission
The F-35A is the U.S. Air Force’s latest fifth-generation fighter. It will replace the U.S. Air Force’s aging fleet of F-16 Fighting Falcons and A-10 Thunderbolt II’s, which have been the primary fighter aircraft for more than 20 years, and bring with it an enhanced capability to survive in the advanced threat environment in which it was designed to operate. With its aerodynamic performance and advanced integrated avionics, the F-35A will provide next-generation stealth, enhanced situational awareness, and reduced vulnerability for the United States and allied nations.
Features
The conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) F-35A gives the U.S. Air Force and allies the power to dominate the skies – anytime, anywhere. The F-35A is an agile, versatile, high-performance, 9g capable multirole fighter that combines stealth, sensor fusion, and unprecedented situational awareness.
The F-35A’s advanced sensor package is designed to gather, fuse and distribute more information than any fighter in history, giving operators a decisive advantage over all adversaries. Its processing power, open architecture, sophisticated sensors, information fusion and flexible communication links make the F-35 an indispensable tool in future homeland defense, Joint and Coalition irregular warfare and major combat operations.

Maj. Justin Robinson flies the 56th Operations Group flagship F-16 Fighting Falcon as he escorts Luke Air Force Base’s first F-35 Lightning II to the base March 10, 2014. The F-35 was flown by Col. Roderick Cregier, an F-35 test pilot stationed at Edwards AFB, Calif. Robin
Because logistics support accounts for two-thirds of an aircraft’s life cycle cost, the F-35 is designed to achieve unprecedented levels of reliability and maintainability, combined with a highly responsive support and training system linked with the latest in information technology. The Autonomic Logistics Information System (ALIS) integrates current performance, operational parameters, current configuration, scheduled upgrades and maintenance, component history, predictive diagnostics (prognostics) and health management, operations scheduling, training, mission planning and service support for the F-35. Essentially, ALIS performs behind-the-scenes monitoring, maintenance and prognostics to support the aircraft and ensure continued health and enhance operational planning and execution.
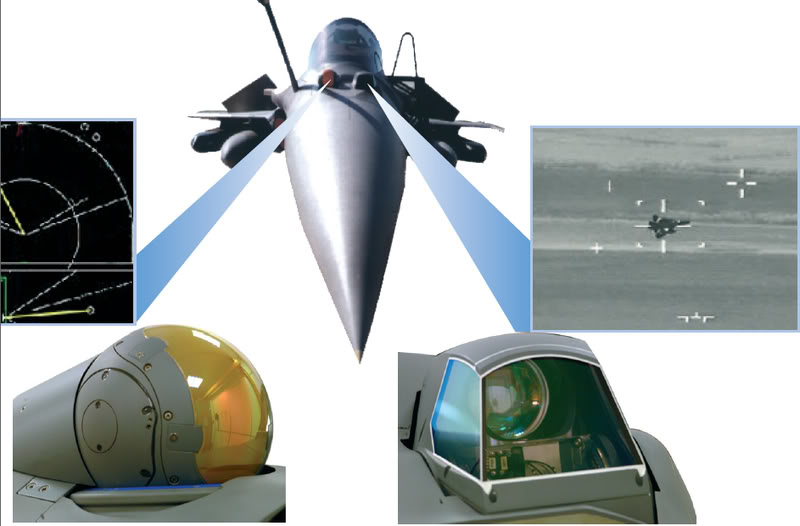
The F-35’s electronic sensors include the Electro-Optical Distributed Aperture System (DAS). This system provides pilots with situational awareness in a sphere around the aircraft for enhanced missile warning, aircraft warning, and day/night pilot vision.. Additionally, the aircraft is equipped with the Electro-Optical Targeting System (EOTS). The internally mounted EOTS provides extended range detection and precision targeting against ground targets, plus long range detection of air-to-air threats.
The F-35’s helmet mounted display system is the most advanced system of its kind. All the intelligence and targeting information an F-35 pilot needs to complete the mission is displayed on the helmet’s visor.
The F-35 contains state-of-the-art tactical data links that provide the secure sharing of data among its flight members as well as other airborne, surface and ground-based platforms required to perform assigned missions. The commitment of JSF partner nations to common communications capabilities and web-enabled logistics support will enable a new level of Coalition interoperability. These capabilities allow the F-35 to lead the defense community in the migration to the net-centric war fighting force of the future.
The F-35’s engine produces 43,000 lbs of thrust and consists of a 3-stage fan, a 6-stage compressor, an annular combustor, a single stage high-pressure turbine, and a 2 stage low-pressure turbine.
The F-35 is designed to provide the pilot with unsurpassed situational awareness, positive target identification and precision strike in all weather conditions. Mission systems integration and outstanding over-the-nose visibility features are designed to dramatically enhance pilot performance.
With nine countries involved in its development (United States, United Kingdom, Italy, Netherlands, Turkey, Canada, Denmark, Norway and Australia), the F-35 represents a new model of international cooperation, ensuring U.S. and Coalition partner security well into the 21st Century. The F-35 also brings together strategic international partnerships, providing affordability by reducing redundant research and development and providing access to technology around the world. Along these lines, the F-35 will employ a variety of US and allied weapons.
Background
The F-35 is designed to replace aging fighter inventories including U.S. Air Force F-16s and A-10s, U.S. Navy F/A-18s, U.S. Marine Corps AV-8B Harriers and F/A-18s, and U.K. Harrier GR.7s and Sea Harriers. With stealth and a host of next-generation technologies, the F-35 will be far and away the world’s most advanced multi-role fighter. There exists an aging fleet of tactical aircraft worldwide. The F-35 is intended to solve that problem.
On October 26, 2001, Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology and Logistics Edward C. “Pete” Aldridge Jr. announced the decision to proceed with the Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) program. This approval advanced the program to the System Development and Demonstration (SDD) phase. The Secretary of the Air Force James G. Roche announced the selection of Lockheed Martin teamed with Northrop Grumman and BAE to develop and then produce the JSF aircraft.
During this SDD phase, the program will focus on developing a family of strike aircraft that significantly reduces life-cycle cost while meeting operational requirements. The requirements represent a balanced approach to affordability, lethality, survivability and supportability. The program will use a phased block approach that addresses aircraft and weapons integration and provides a validated and verified air system for Initial Operational Capability requirements.
General Characteristics
Primary Function: Multirole fighter
Prime Contractor: Lockheed Martin
Power Plant: One Pratt & Whitney F135-PW-100 turbofan engine
Thrust: 43,000 pounds
Wingspan: 35 feet (10.7 meters)
Length: 51 feet (15.7 meters)
Height: 14 feet (4.38 meters)
Maximum Takeoff Weight: 70,000 pound class
Fuel Capacity: Internal: 18,498 pounds
Payload: 18,000 pounds (8,160 kilograms)
Speed: Mach 1.6 (~1,200 mph)
Range: More than 1,350 miles with internal fuel (1,200+ nautical miles), unlimited with aerial refueling
Ceiling: Above 50,000 feet (15 kilometers)
Armament: Internal and external capability. Munitions carried vary based on mission requirements.
Crew: One
More from Breaking Defense
http://breakingdefense.com/2015/07/f-16-vs-f-35-in-a-dogfight-jpo-air-force-weigh-in-on-whos-best/
VIDEO DISCOVERY
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II (also known as the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter) is a family of single-seat, single-engine, fifth-generation multirole fighters under development to perform ground attack, reconnaissance, and air defense missions with stealth capability. The F-35 has three main models; the F-35A is a conventional takeoff and landing variant, the F-35B is a short take-off and vertical-landing variant, and the F-35C is a carrier-based variant.
AF F-35 Lightening Video Published on Apr 17, 2013
Multimedia package showcasing the F-35A Lighting II capabilities integrated with the US Air Force Warfare Center mission. The F-35A is a multirole fighter aircraft designed to supplement and eventually replace the F-16 and A-10 and complement the F-22.
https://www.sofmag.com/f-35-vs-f-16/
لاف 35 نازلت الاف 16 بالفعل لكن تفوقت الاف 16
F16 انتصرت على F35
و F15 انهزمت من F35 بنتيجة 8 / 0
سبحان الله
دائما F16 والرافال متفوقات على جميع مايطير في الهواء حتى على الاطباق الفضائية
و F15 والتايفون فاشلات في جميع الاحوال :لا تعليق:
اعتقد حتى الميراج متفوقة جدا على F15 والتايفون :;:
خلك موضوعي يا اخ كاميكازي ..

Leak photo showed US piloted F-22 "shot" down by a Malaysian piloted Mig-29 during the recent Exercise Cope Taufan in Malaysia. The photo showed the F-22 failed to radar jam the Mig and was releasing flares to avoid missile lock-on by the Mig-29, but was later nailed by cannon fire instead.
It was reported the Mig was piloted by a Malaysian-Chinese pilot who claimed the F-22 was in ambush mode while going stealth (in passive mode) with no radar emission and using a F-15 to bait the Malaysian jets, but he could detect it with the new Russian radar installed last year.
Photo was taken by helmet-cam from a F-15 which was trying to assist the F-22. It breaks off after the F-22 was nailed as another F-29 tried to radar lock him.
Embedded media from this media site is no longer available
هل هذه الصورة صحيحة
الصورة توضح f22 تطلق شعلات حرارية لتخلص من اطباق mig 29n الماليزية و التي نجحت الاخيرة في تسجيل اصابة باستخدام المدفع الرشاش خلال مناورات Exercise Cope Taufan in Malaysia.
F15 ليست mig29
Leak photo showed US piloted F-22 "shot" down by a Malaysian piloted Mig-29 during the recent Exercise Cope Taufan in Malaysia. The photo showed the F-22 failed to radar jam the Mig and was releasing flares to avoid missile lock-on by the Mig-29, but was later nailed by cannon fire instead.
It was reported the Mig was piloted by a Malaysian-Chinese pilot who claimed the F-22 was in ambush mode while going stealth (in passive mode) with no radar emission and using a F-15 to bait the Malaysian jets, but he could detect it with the new Russian radar installed last year.
Photo was taken by helmet-cam from a F-15 which was trying to assist the F-22. It breaks off after the F-22 was nailed as another F-29 tried to radar lock him.
Embedded media from this media site is no longer available
هل هذه الصورة صحيحة
الصورة توضح f22 تطلق شعلات حرارية لتخلص من اطباق mig 29n الماليزية و التي نجحت الاخيرة في تسجيل اصابة باستخدام المدفع الرشاش خلال مناورات Exercise Cope Taufan in Malaysia.
https://theaviationist.com/2014/06/18/close-aerial-combat-f15-f22/هذه Mig29 وليست F-15
انظر لاختلاف ال Air intake وهو بارز من اسفل المقاتلة فى الميج 29 على العكس من ال F-15
F16 انتصرت على F35
و F15 انهزمت من F35 بنتيجة 8 / 0
سبحان الله
دائما F16 والرافال متفوقات على جميع مايطير في الهواء حتى على الاطباق الفضائية
و F15 والتايفون فاشلات في جميع الاحوال :لا تعليق:
اعتقد حتى الميراج متفوقة جدا على F15 والتايفون :;:
خلك موضوعي يا اخ كاميكازي ..
انا مجرد ناقل للاخبار بمصادرها ولست القي الاحكام هنا ... التفوق بالطبع سيكون للمعدة الافضل .. وانا لست خبيرا بل مجرد هاوي يحب القراءة فحسب ..
ليس بالشيء الغريب فالاف-15 مقاتله من الجيل الرابع بينما الاف-35 جيل خامس وقريباً سنراها في القوات الجويه الملكيه السعوديه
وكلنا نعرف ان الاف-15 تتفوق على السو-35 ..
وان الاف-35 تفوقت على الاف-15 ..
فتخليوا معي مواجهه بين الاف-35 والسو-35 !!!!!!!!
وكلنا نعرف ان الاف-15 تتفوق على السو-35 ..
وان الاف-35 تفوقت على الاف-15 ..
فتخليوا معي مواجهه بين الاف-35 والسو-35 !!!!!!!!
المواضيع المشابهة
- New replies moderating enabled
- الردود
- 142
- المشاهدات
- 15K
- الردود
- 3
- المشاهدات
- 1K
- الردود
- 3
- المشاهدات
- 2K
- الردود
- 7
- المشاهدات
- 4K
- الردود
- 6
- المشاهدات
- 7K