هل بالامكان التوضيح أكثر؟
- تطوير نظم الأستقبال و الملاحة في الدول العربية
- تدريب الكوادر الفنية
- نقل التقنيات الفضائية الى الدول العربية
- تدريب الكوادر الفنية
- نقل التقنيات الفضائية الى الدول العربية
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
ملاحظة: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
هل بالامكان التوضيح أكثر؟
منظومة غاليليو لم تكتمل حتى هذه الساعة!
The first Galileo test satellite, the GIOVE-A, was launched 28 December 2005, while the first satellite to be part of the operational system was launched on 21 October 2011. As of December 2016 the system has 18 of 30 satellites in orbit. Galileo started offering Early Operational Capability (EOC) on 15 December 2016[1] and is expected to reach Full Operational Capability (FOC) in 2019.[8] The complete 30-satellite Galileo system (24 operational and 6 active spares) is expected by 2020.[9]
التوجه السعودي كان منذ 2006 وليس التطبيق العملي لأنه لم يتم حتى الأن
عموماً النظام وصل الى القدرة التشغيلية الأولية (EOC) في 15 ديسمبر 2016
و سيصل بأذن الله إلى القدرة التشغيلية الكاملة (FOC) في عام 2019.
Besides the ESA member states, numerous other countries are involved in Galileo in one way or another. Among them are India, Israel, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, South Korea and Ukraine.
The EU's stance is that Galileo is a neutral technology, available to all countries and everyone. At first, EU officials did not want to change their original plans for Galileo, but have since reached a compromise, that Galileo was to use a different frequency. This allowed the blocking or jamming of either GNSS without affecting the other (jam Galileo without affecting GPS, or jam GPS but not Galileo), giving the US a greater advantage in conflicts in which it has the electronic warfare upper hand.[19]
In spite of this mission cooperation between China and Saudi Arabia in space industry will be developed and will be extended also on common efforts to develop reception system in Saudi Arabia for new Chinese navigation system called Beidou. Under this agreement, King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST), main scientific organization is Saudi Arabia, will be responsible to create common reception system for Beidou and GPS. Of course part of system which will be utilized for receiving Beidou signal will be designed and developed in the close cooperation with China. Agreement with China was signed six months after King Salman signed similar but more general agreement with Roscosmos. It will be first Saudi research satellite launched by Chinese company and proof of strong position of China in Arab countries (all previous were lifted on atop Dnepr rockets).
وأشارإلى أن مدينة الملك عبدالعزيز للعلوم والتقنية سوف تعمل بالتعاون مع مكتب الملاحة بالأقمار الاصطناعية الصيني على دراسات علمية لتطوير أنظمة استقبال واستخدام نظام الملاحة بالأقمار الاصطناعية الصيني "بايدو" المشابهة لنظام الملاحة العالمي "GPS" للعمل بكفاءة أعلى في المملكة عبر الأبحاث المشتركة التي تشمل مراقبة النظام، وتقويم الأداء والأنظمة التكاملية.
مشاركه سابقه ل صديقي@Senator
G @GSN
اعتقد ان هذه المصادر أكثر من كافيه..


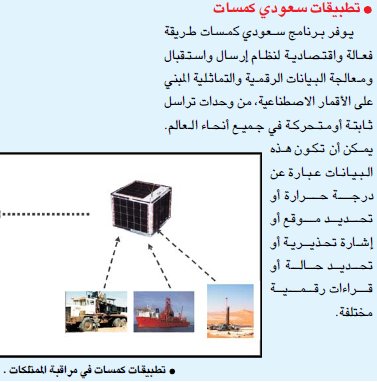

أولا: التقرير يتحدث عن أقمار تجارية وليست عسكرية؟عموما المملكة لها محاولات سابقه للإستغناء عن الأقمار الأمريكيه خاصه في العمليات العسكريه ومن ضمنها الإستغناء عن ال GPS في تحديد المواقع سواء المدنية أو العسكريه عن طريق تصنيع مجموعه من الأقمار الإصطناعيه وإطلاقها .
وهي مجموعة أقمار سعودي كمسات وهي من إنتاج مدينة الملك عبدالعزيز للعلوم والتقنيه




انا لو اهرول زياده جبت العجب مير مهدي اللعب..
أولا: التقرير يتحدث عن أقمار تجارية وليست عسكرية؟
ثانيا: ماهي المهام التي يمكن أن تستخدم فيه؟ هل بالإمكان استخدامها على المقاتلات او في توجيه الصواريخ؟
